Communication Impairment in Aphasia Patients: A Neuropragmatic Study
##semicolon##
https://doi.org/10.21271/zjhs.28.SpC.21##semicolon##
Aphasia, Communication Impairment, Neuropragmatics, Pragmatics.پوختە
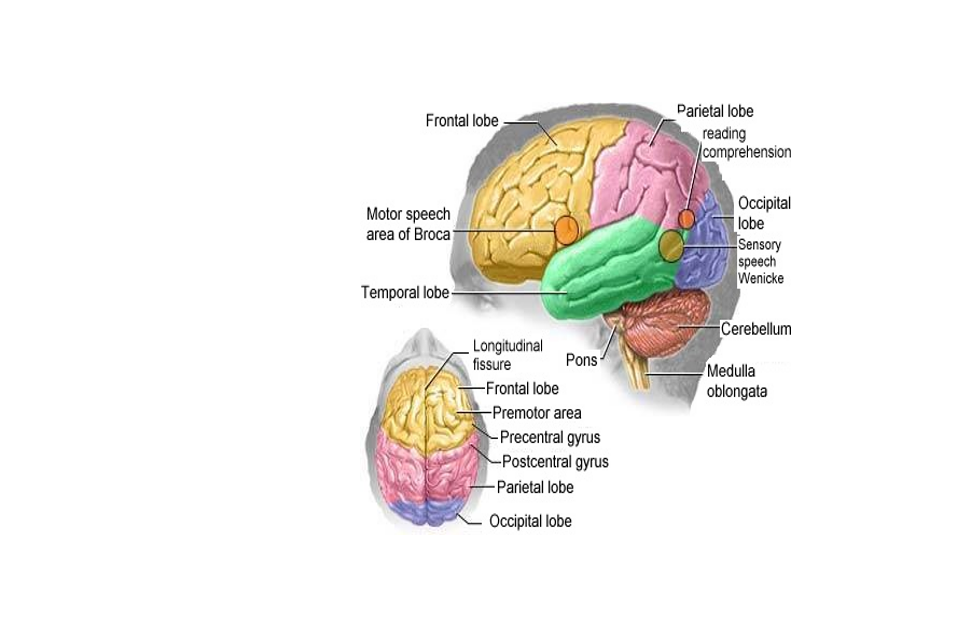
This paper is an attempt to introduce the theoretical concepts relating to the relationship between the brain and communication. It aims to explore communication difficulties experienced by individuals with aphasia. Using a neuropragamtic analysis, it investigates the challenges the aphasia patients face in their attempts to convey meaning within various communicative contexts. By showing how linguistic impairments intersect with pragmatic skills, this study enhances the understating of pragmatic processing in those with neurological impairments. In defining communication impairment, a neurological foundation of language in the brain is clarified. All the areas responsible for producing and comprehending language are presented along with explaining how lesions to the areas result in different language disorders. The last part of the study is devoted to the study of pragmatics from a neurological perspective where there is a description of the pragmatic skills of people who suffer from a brain injury. The emphasis, however, is on conversation as a major type of interpersonal communication to show how the cooperative principle and the maxims as the basic concepts of pragmatics are affected by aphasia which results in communication impairment.
سەرچاوەکان
- Ahlsén, E. (1993). Conversational principles and aphasic communication. Journal of
- Pragmatics, 19, 57-70.
- Ahlsén, E. (2006). Introduction to Neurolinguistics. John Benjamin Publishing Company.
- Aitchison, J. (1999). Linguistics. London: Hodder Education
- Aitchison, J. (2008). The Articulate Mammal: An Introduction to Psycholinguistics. London: Routledge.
- Akmajian, A.; Demers, R, A.; Farmer, A.K.; Harnish, R.M. (2001). An Introduction to Language and Communication. Cambridge: MIT Press.
- Bambini, V. (2012). Neuropragmatics. In Östman J-O & Verschueren J. (Eds.), Handbook of Pragmatics (pp.1-21). Benjamins.
- Bambini, V., & Bara, B. G. (2012). Neuropragmatics. In J.-O. Östman & J. Verschueren
- (Eds.), Handbook of Pragmatics (pp. 1–21). John Benjamins Publishing Company.
- https://doi.org/10.1075/hop.16.neu2
- Bambini, V., & Domaneschi, F. (2017). Behavioral and Neural Evidence on Pragmatic Processing. Frontiers in Psychology, 1. doi: 10.3389/conf.fpsyg.2017.71.00001
- Blake, M. (2021). Communication Deficits Associated with Right Hemisphere Brain Damage. In Damico, J., Muller, N., and Ball, M (Ed.s), The Handbook of Language and Speech Disorder ( pp. 571-589). John Wiley& Sons Ltd.. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119606987.ch24
- Caplan, D., & Waters, G. (2003). Online syntactic processing in aphasia: studies with auditory moving window presentation. Brain and language, 84(2), 222–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0093-934x(02)00514-x
- Chang E. F., Raygor K. P., Berger M. S. (2015). Contemporary model of language organization: an overview for neurosurgeons. Journal of Neurosurgery. 122(2):250–261. doi: 10.3171/2014.10.JNS132647.
- Chapman, S., Highley, A., Thompson, J. (1998). Discourse in fluent aphasia and Alzheimer's disease: Linguistic and pragmatic considerations. Journal of Neurolinguistics, Volume 11, Issues 1–2, Pages 55-78. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0911-6044(98)00005-0
- Collinge, N.E. (1990). An Encyclopedia of Language. London: Routledge.
- Cruse, A. (2000). Meaning in Language: An Introduction to Semantics and Pragmatics. Oxford: Oxford University Press
- Cruse, A. (2006). A Glossary of Semantics and Pragmatics. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press.
- Crystal, D. (1997). The Cambridge Encyclopedia of Language. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Cummings, L. (2012). Pragmatic Disorders. In Schmid, H. (ed.), Cognitive Pragmatics: Handbook of Pragmatics (291-315). Berlin and Boston: Walter de Gruyter.
- Cummings, L. (2017). Clinical linguistics. In M. Aronoff (ed.), Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Linguistics. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Cummings, L. (2017). Clinical Pragmatics. In Yueguo, G. Barron, A. & Steen, G. (eds), Routledge Handbook of Pragmatics (pp.419-432). London and New York: Routledge.
- Davidson, B., Howe, T., Worrall, L., Hickson, L., Togher, L. (2008). Social participation for older people with aphasia: the impact of communication disability on friendships. Topics in stroke rehabilitation, 15(4), 325-340. doi: 10.1310/tsr1504-325
- Davis, B & Guenddouzi, J. (2013). Pragmatics in Dementia Discourse. Newcastle upon Tyne: Cambridge Scholars Publishing
- Dronkers, N., Ludy, C. Redfern, B. (1998). Pragmatics in the absence of verbal language: Descriptions of a severe aphasic and a language-deprived adult. Journal of Neurolinguistics,11, 1–2, Pages 179-190. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0911-6044(98)00012-8
- Field, J. (2004). Psycholinguistics: The Key Concepts. London: Routledge.
- Fridriksson J., den Ouden D. B., Hillis A. E. (2018). Anatomy of aphasia revisited. Brain.141(3):848–862. doi: 10.1093/brain/awx363
- Gallagher, T. & Prutting, C. (1983). Pragmatic assessment and intervention issues in language. San Diego, CA: College-Hill Press
- Hagoort, P. (2017). The Core and Beyond in the language-ready Brain, Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, Volume 81, Part B, pp 194-204.
- Harris, R. (1996). Signs, Language and Communication: Integrational and segregational approaches. London: Routledge.
- Hickok, G. & Poeppel, D. (2003). Dorsal and ventral streams: a framework for understanding aspects of the functional anatomy of language. Cognition. 92(1-2):67–99. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2003.10.011.
- Hickok, G. & Poeppel, D. (2004). Towards a new functional anatomy of language. Cognition. 92(1-2):1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2003.11.001.
- Hickok, G. & Poeppel, D. (2015). Neural basis of speech perception. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. 129:149–160. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-62630-1.00008-1.
- Hogg, MA, Vaughan, GM. (2008). Social Psychology (5th ed.). London: Pearson Education Limited, London. Holmes J. (2001). An introduction to sociolinguistics (2nd ed.). Harlow, UK: Pearson Education.
- Ingram, J. (2007). Neurolinguistics: An Introduction to Spoken Language Processing and its Disorders. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
- Johansson, M., Carlsson, M., Sonnander, K. (2012). Communication difficulties and the use of communication strategies: From the perspective of individuals with aphasia. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders 47(2):144-55 http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-6984.2011.00089.x
- Kümmerer D., Hartwigsen G., Kellmeyer P. (2013). Damage to ventral and dorsal language pathways in acute aphasia. Brain.;136(2):619–629. doi: 10.1093/brain/aws354.
- Locher, MA. (2010). Relational work, politeness, and identity construction. In Matsumoto D (Ed.), Handbook of interpersonal communication (pp. 111- 138). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
- Lock, S. Wilkinson, R., Bryan, K., Maxim, J., Edmundson, A., Bruce, C. (2001). Supporting Partners of People with Aphasia in Relationships and Conversation (SPPARC). International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders, 36(s1), 25-30. doi:10.3109/13682820109177853
- Lyons, J. (1981). Language and Linguistics. London: Cambridge University Press
- McNamara, P., & Durso, R. (2003). Pragmatic communication skills in patients with Parkinson's disease. Brain and Language, 84(3), 414–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0093-934X(02)00558-8.Mead GH. (1962). Mind, self and society: from the standpoint of a social behaviorist. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Munro, F. (2003). Macleod's Clinical Examination. London: Harcourt Publishers.
- Mosquera, C., Vazquez, A. & Malanda, A. (2012). EEG Signal Processing for Epilepsy. http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/31609
- Nasios, G., Dardiotis, E., & Messinis, L. (2019). From Broca and Wernicke to the Neuromodulation Era: Insights of Brain Language Networks for Neurorehabilitation. Behavioural neurology, 9894571. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9894571
- Paradis, M. (1998). Pragmatics in Neurogenic Communication Disorders. Oxford: Pergamon Press.
- Perkins, M. (2011). In Östman, J.-O., & Verschueren, J. (Eds.), Pragmatics in practice. (Handbook of Pragmatics Highlights; Vol. 9). (pp. 66-92). John Benjamins. http://benjamins.com/#catalog/books/hoph/main
- Sacks, H., Schegloff, EA., Jefferson, G. (1974). The simplest systematics for the organization of turn-taking for conversation. Language, 50(4), 696-735.
- Saur, D., Kreher, B. W., Schnell, S. (2008). Ventral and dorsal pathways for language. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 105(46):18035–18040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0805234105.
- Schiffrin, D. (1988). Conversation analysis. Annual review of applied linguistics, 11, 3-16.
- Shedlon, J. (2019). Retrieved from https://www.bbtrial.com/blog/brain-injuries-traumatic-vs-non-traumatic/ on June 17, 2022
- Small, S. L. (2008). The neuroscience of language. Brain and language, 106(1), 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandl.2008.05.004
- Stemmer, B. (1999) Pragmatics: Theoretical and Clinical Issues. Special Issues of Brain and Language 68.
- Stemmer, B. (2008). Neuropragmatics, Disorders and Neural Systems. In Stemmer, B. and Whiteaker, H.A. (Eds). Handbook of the Neuroscience of Language (367-379). Cambridge, MA: Elsevier.
- Struchen, M. A., Pappadis, M. R., Sander, A. M., Burrows, C. S., & Myszka, K. A. (2011). Examining the contribution of social communication abilities and affective/behavioral functioning to social integration outcomes for adults with traumatic brain injury. The Journal of head trauma rehabilitation, 26(1), 30–42. https://doi.org/10.1097/HTR.0b013e3182048f7c
- Swash, M. (1997). Hutchison's Clinical Methods. London: W.B. Saunders Company.
- Toledo, J., Lizcano-Cortés, F., Olalde-Mathieu, V. E., Licea-Haquet, G., Zamora-Ursulo, M. A., Giordano, M., & Reyes-Aguilar, A. (2021). A Dataset to Study Pragmatic Language and Its Underlying Cognitive Processes. Frontiers in human neuroscience, 15, 666210. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2021.666210
- Trask, R.L. (1999). Language: the Basics. London: Routledge.
- Traxler, M. J. & Gernsbacher, M.A.(2006). Handbook of Psycholinguistics. London: Elsevier Inc.
- Trembley P., Dick A. S. (2016) Broca and Wernicke are dead, or moving past the classic model of language neurobiology. Brain and Language. 162:60–71. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2016.08.004.
- Weber, T. (2010). Everyday communication and socializing. In Matsumoto D (Ed.), APA Handbook of interpersonal communication (pp. 187-214).
- Wilkinson, R. (2011). Changing the talk of people with aphasia in everyday conversations: research evidence and clinical issues. Paper presented at the 3rd Nordic Aphasia Conference, Helsinki, Finland.
- Yule, G. (1996). Pragmatics. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
##submission.downloads##
بڵاو کرایەوە
ژمارە
بەش
##submission.license##
##submission.copyrightStatement##
##submission.license.cc.by4.footer##








