Application of nanotechnology for remediation drill cutting soil
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21271/ZJPAS.35.4.12Keywords:
Keyword: drill cutting, heavy metal, nanotechnology, petroleum hydrocarbonsAbstract
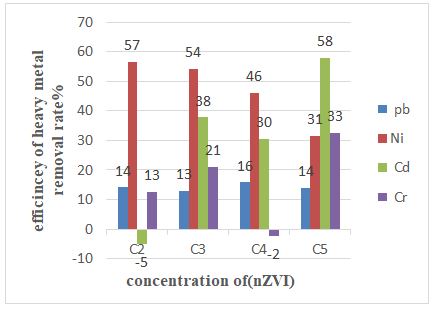
This study was carried out for remediation of drill cutting soil from two oil field sites in Kurdistan Region of Iraq. nanotechnology was implemented. Heavy metal (Pb, Cd, Cr, Ni and petroleum hydrocarbons (C8-C24, C24-C40, TPH) were analyzed before and after remediation drill cutting soil. The experiment was designed. The results indicate that the concentration of heavy metals (Ni, Cd and Cr) was within the normal range except the concentration of Pb. The result showed that the removal rate of heavy metal by nano technic was (Pb%16, Ni %57, Cd% 48, Cr%38). And the removal rate of hydrocarbons was (TPH%57, C8-C24%62, C24-C40%41). these means the (nZVI) has effect for minimizing heavy metal and petroleum hydrocarbons in drill cutting soil.
References
AHMAD, A. A., MUHAMMAD, I., SHAH, T., KALWAR, Q., ZHANG, J., LIANG, Z., MEI, D., JUANSHAN, Z., YAN, P., ZHI, D. J. W. J. O. A. & SCIENCE, S. 2020. Remediation methods of crude oil contaminated soil. 4, 8.
AHMAD, T. A. & GANJO, D. G. J. E. J. O. B. 2020. Fungal isolates and their bioremediation for pH, chloride, tph and some toxic heavy metals. 14, 149-160.
AMIN, S. A., AL-OBIADY, A., ALANI, R. R. & AL-MASHHADY, A. A. J. E. T. J. 2018. Assessment of some heavy metal concentrations in drilling mud samples in Az Zubair oil field, Basra, Iraq. 36, 68-75.
CHANG, M.-C., SHU, H.-Y., HSIEH, W.-P., WANG, M.-C. J. J. O. T. A. & ASSOCIATION, W. M. 2007. Remediation of soil contaminated with pyrene using ground nanoscale zero-valent iron. 57, 221-227.
CUNDY, A. B., HOPKINSON, L. & WHITBY, R. L. J. S. O. T. T. E. 2008. Use of iron-based technologies in contaminated land and groundwater remediation: A review. 400, 42-51.
DHIMAN, A. S. J. M. S., DALHOUSE UNIVERSITY 2012. Rheological properties & corrosion characteristics of drilling mud additives.
FELIX, O., NWAOGAZIE, I. L., AKARANTA, O. & ABU, G. O. 2018. Removal of Heavy Metals In Spent Synthetic-Based Drilling Mud Using Nano Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI).
FRANCY, N., SHANTHAKUMAR, S., CHIAMPO, F. & SEKHAR, Y. R. J. P. 2020. Remediation of lead and nickel contaminated soil using nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) particles synthesized using green leaves: First results. 8, 1453.
HENN, K. W., WADDILL, D. W. J. R. J. T. J. O. E. C. C., TECHNOLOGIES & TECHNIQUES 2006. Utilization of nanoscale zero‐valent iron for source remediation—A case study. 16, 57-77.
ISMAIL, A. R., ALIAS, A., SULAIMAN, W., JAAFAR, M. & ISMAIL, I. J. C. E. T. 2017. Drilling fluid waste management in drilling for oil and gas wells. 56, 1351-1356.
JAMROZIK, A., WISNIOWSKI, R. & GONET, A. J. I. M. S. G. S. 2019. The best available techniques for the control of solids and treatment of oil-contaminated drilling waste. 19, 1099-1107.
KUMPIENE, J., ORE, S., RENELLA, G., MENCH, M., LAGERKVIST, A. & MAURICE, C. J. E. P. 2006. Assessment of zerovalent iron for stabilization of chromium, copper, and arsenic in soil. 144, 62-69.
LODUNGI, J. F., ALFRED, D., KHIRULTHZAM, A., ADNAN, F. & TELLICHANDRAN, S. J. I. J. O. W. R. 2016. A review in oil exploration and production waste discharges according to legislative and waste management practices perspective in Malaysia. 7, 260.
MIKOS-SZYMAŃSKA, M., RUSEK, P., BOROWIK, K., ROLEWICZ, M., BOGUSZ, P., GLUZIŃSKA, J. J. E. S. & RESEARCH, P. 2018. Characterization of drilling waste from shale gas exploration in Central and Eastern Poland. 25, 35990-36001.
MORAIS, S., COSTA, F. G., PEREIRA, M. D. L. J. E. H. E. I. & PRACTICE 2012. Heavy metals and human health. 10, 227-245.
MURGUEITIO, E., CUMBAL, L., ABRIL, M., IZQUIERDO, A., DEBUT, A. & TINOCO, O. J. J. O. N. 2018. Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles: Application on the removal of petroleum oil from contaminated water and soils. 2018.
NOUBACTEP, C., CARÉ, S., CRANE, R. J. W., AIR, & POLLUTION, S. 2012. Nanoscale metallic iron for environmental remediation: prospects and limitations. 223, 1363-1382.
O’CARROLL, D., SLEEP, B., KROL, M., BOPARAI, H. & KOCUR, C. J. A. I. W. R. 2013. Nanoscale zero valent iron and bimetallic particles for contaminated site remediation. 51, 104-122.
ONWUKWE, S., NWAKAUDU, M. J. I. J. O. E. S. & DEVELOPMENT 2012. Drilling wastes generation and management approach. 3, 252.
SABIENË, N., BRAZAUSKIENË, D. M. & RIMMER, D. J. E. 2004. Determination of heavy metal mobile forms by different extraction methods. 1, 36-41.
SINGH, J., KALAMDHAD, A. S. J. I. J. O. R. I. C. & ENVIRONMENT 2011. Effects of heavy metals on soil, plants, human health and aquatic life. 1, 15-21.
SUN, Y., ZHENG, F., WANG, W., ZHANG, S. & WANG, F. J. T. 2020. Remediation of Cr (VI)-contaminated soil by nano-zero-valent iron in combination with biochar or humic acid and the consequences for plant performance. 8, 26.
TOWNEND, J. 2013. Practical statistics for environmental and biological scientists, John Wiley & Sons.
TRATNYEK, P. G. & JOHNSON, R. L. J. N. T. 2006. Nanotechnologies for environmental cleanup. 1, 44-48.
ZHANG, M., WANG, Y., ZHAO, D. & PAN, G. J. C. S. B. 2010. Immobilization of arsenic in soils by stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron, iron sulfide (FeS), and magnetite (Fe 3 O 4) particles. 55, 365-372.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Zhakaw kamal Abdullah, Dalshad Azeez Darwesh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.













