MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS USING GEO-INFORMATION TECHNIQUES FOR BASTORA BASIN NORTH EAST OF ERBILCITY IRAQI KURDISTAN REGION
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21271/ZJPAS.35.3.11Keywords:
Bastora Basin, Morphometry, Basin, Stream, River, Drainage, produce, Northern Iraq.Abstract
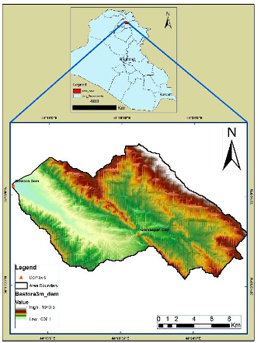
The current study aims to conduct a detailed morphometric investigation of the Bastora basin watersheds in the northeastern section of Erbil, Iraq. The study region is situated between the longitudes of 44o 10' 19" and 44o 27' 33" east and the latitudes of 36o 19' 36" to 36o 15' 17" north. The present research attempts to study detail morphometric analysis of Bastora basin watersheds in the northeastern To meet the goals of this study, the areas of the basins are 236.4 Km2. Geo-information (Remote sensing and GIS) techniques were utilized to determine and analyze morphometric characteristics in terms of linear, aerial, and relief aspects. Several tools in the ArcGIS 10.8 program were used to prepare and produce maps, analyze and evaluate various parameter features, and enforce specification hydrology tool. An area was covered by a six-order drainage sub-basin with a total of (587) streams and (418.24 km) of stream length. Just the mean bifurcation ratio (3.62). The sixth order sinuosity index value is (1.4). The results were (1.77 km-1 for drainage density and 6.00 for drainage texture. The circulation ratio is and the elongation ratio is (0.31). The extended morphology, low runoff discharge, and high subsurface permeability of the basin imply these characteristics. The river can be thought of as the average stage of balance between erosion and sediment deposition. The hydro-morphometric analysis is a very helpful guide for choosing the location and type of dam.
References
• Al-ASSADI, K.H., 2015. Morphometric analysis of characteristics of the Rabaish Basin in the Najaf Province by using GIS. University of Kufa. Literature College. Vol.1, No.25, p. 274 – 253 (in Arabic).
• Adhikari, S., 2020. Morphometric Analysis of a Drainage Basin: A Study of Ghatganga River, Bajhang District, Nepal. The Geographic Base, 7, pp.127-144.
• Ali, S.A. and Khan, N., 2013. Evaluation of morphometric parameters—a remote sensing and GIS based approach.
• Ali, U., Ali, S.A., Yousuf, M., Rasool, Q.A., Ahmad, M. and Ahmad, I., 2021. Consideration of geomorphic indices in assessment of relative active tectonics in a part of seismogenic compressional Kashmir Basin. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 14(13), pp.1-15.
• Arabameri, A., Rezaei, K., Pourghasemi, H.R., Lee, S. and Yamani, M., 2018. GIS-based gully erosion susceptibility mapping: a comparison among three data-driven models and AHP knowledge-based technique. Environmental earth sciences, 77(17), pp.1-22.
• Aravinda, P.T. and Balakrishna, H.B., 2013. Morphometric analysis of vrishabhavathi watershed using remote sensing and GIS. Int. J. Res. Eng. Tech, 2(8), pp.514-522.
• Charlton, R., 2007. Fundamentals of fluvial geomorphology. Routledge, pp. 280.
• Chitra, C., Alaguraja, P., Ganeshkumari, K., Yuvaraj, D. and Manivel, M., 2011. Watershed characteristics of Kundah sub basin using remote sensing and GIS techniques. International Journal of geomatics and geosciences, 2(1), p.311.
• Chorley, R.J., Malm, D.E. and Pogorzelski, H.A., 1957. A new standard for estimating drainage basin shape. American journal of science, 255(2), pp.138-141.
• El Hamdouni, R., Irigaray, C., Fernández, T., Chacón, J. and Keller, E.A., 2008. Assessment of relative active tectonics, southwest border of the Sierra Nevada (southern Spain). Geomorphology, 96(1-2), pp.150-173.
• Farhan, Y., Anbar, A., Enaba, O. and Al-Shaikh, N., 2015. Quantitative analysis of geomorphometric parameters of Wadi Kerak, Jordan, using remote sensing and GIS. Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 7(06), p.456.
• Fatah, K.K., Seeyan, S. and Jirjees, S., 2020. Morphometric analysis using geo-information techniques for different watersheds in northeastern part of Erbil City, Kurdistan Region, North Iraq. The Iraqi Geological Journal, pp.88-104.
• Gregory, K.J. and Walling, D.E., 1973. Drainage basin form and process.
• Hack, J.T., 1973. Stream-profile analysis and stream-gradient index. Journal of Research of the us Geological Survey, 1(4), pp.421-429.
• Hare, P.W. and Gardner, T.W., 1985. Geomorphic indicators of vertical neotectonism along converging plate margins, Nicoya Peninsula, Costa Rica. Tectonic geomorphology, 4, pp.75-104.
• Horton, R.E., 1932. Drainage basin characteristics, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 13(1), 350-361.
• Horton, R.E., 1945. Erosional development of streams and their drainage basins; hydrophysical approach to quantitative morphology. Geological society of America bulletin, 56(3), pp.275-370.
• Ibrahim, S.A., 2019. MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF THE AL-TEEB RIVER BASIN, SE IRAQ, USING DIGITAL ELEVATION MODEL AND GIS. Iraqi Bulletin of Geology and Mining, 15(1), pp.59-69.
• Keller, E.A., 1986. Investigation of active tectonics: use of surficial earth processes. Active tectonics, 1, pp.136-147.
• KELLER, E.A., PINTER, N. (Eds.), 2002. Active Tectonics: Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape, 2nd ed. Prentice Hall,
Upper Saddle River, N.J, p. 362.
• Khare, D., Mondal, A., Mishra, P.K., Kundu, S. and Meena, P.K., 2014. Morphometric analysis for prioritization using remote sensing and GIS techniques in a hilly catchment in the state of Uttarakhand, India. Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 7(10), pp.1650-1662.
• Kumar, N., 2013. Morphometric analysis of river catchments using remote sensing and GIS (a case study of the Sukri River, Rajasthan). International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, 3(6), pp.1-6.
• Mahmood, S.A. and Gloaguen, R., 2012. Appraisal of active tectonics in Hindu Kush: Insights from DEM derived geomorphic indices and drainage analysis. Geoscience Frontiers, 3(4), pp.407-428.
• Miller, V.C., 1953. A QUANTITATIVE GEOMORPHIC STUDY OF DRAINAGE BASIN CHARACTERISTICS IN THE CLINCH MOUNTAIN AREA VIRGINIA AND TENNESSEE. Columbia Univ New York.
• Nag, S.K. and Chakraborty, S., 2003. Influence of rock types and structures in the development of drainage network in hard rock area. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 31(1), pp.25-35.
• Nanda, A.M., Pervez, A., Kanth, T.A. and Hajam, R.A., 2014. Morphometric Analysis of Sandran Drainage Basin (J & K) Using Geo-spatial Technology. Earth Science India, 7.
• Sakthivel, R., Jawahar Raj, N., Sivasankar, V., Akhila, P. and Omine, K., 2019. Geo-spatial technique-based approach on drainage morphometric analysis at Kalrayan Hills, Tamil Nadu, India. Applied Water Science, 9(1), pp.1-18.
• Selvan, M.T., Ahmad, S.A.R.F.A.R.A.Z. and Rashid, S.M., 2011. Analysis of the geomorphometric parameters in high altitude glacierised terrain using SRTM DEM data in Central Himalaya, India. ARPN journal of science and technology, 1(1), pp.22-27.
• Schmid, C. and Mohr, R., 1997. Local grayvalue invariants for image retrieval. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 19(5), pp.530-535.
• Schumm, S., 1956. Evaluation of drainage systems and slopes in Perth Amboy, New Jersey. Geological Society of American Bulletin, 67, pp.597-646.
• Schumm, S.A., Dumont, J.F. and Holbrook, J.M., 2000. Active tectonics and alluvial rivers (Vol. 276). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
• Singh, S. and Singh, M.C., 1997. Morphometric analysis of Kanhar river basin. National geographical Journal of india, 43(1), pp.31-43.
• Smith, K.G., 1950. Standards for grading texture of erosional topography. American journal of Science, 248(9), pp.655-668.
• Sreedevi, P.D., Owais, S.H.H.K., Khan, H.H. and Ahmed, S., 2009. Morphometric analysis of a watershed of South India using SRTM data and GIS. Journal of the geological society of india, 73(4), pp.543-552.
• Srinivasa Vittala, S., Govindaiah, S. and Honne Gowda, H., 2004. Morphometric analysis of sub-watersheds in the Pavagada area of Tumkur district, South India using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 32(4), pp.351-362.
• Stahler, A., 1952. Hypsometric (area altitude) analysis of erosional topology. Geol Soc Am Bull, 63, pp.1117-1142.
• Strahler, A.N. and Chow, V.T., 1964. Handbook of applied hydrology. Quantitative geomorphology of drainage basins and channel networks, pp. 39-76.
• Strahler, A.N., 1968. Quantitative geomorphology. The encyclopedia of geomorphology, pp.898-911.
• Rawat, U., Awasthi, A., Gupta, D.S., Paul, R.S. and Tripathi, S., 2017. Morphometric analysis using remote sensing and GIS techniques in the Bagain River Basin, Bundelkhand Region, India. Indian J. Sci. Technol, 10(10).
• Ritter, M.E., 2006. The physical environment: An introduction to physical geography. Date visited July, 25, p.2008.
• Wood, W.F., 1960. A quantitative system for classifying landforms. Headquarters, Quartermaster Research and Engineering Command, US Army, Quartermaster Research & Engineering Center.
• Zhang, L. and Guilbert, E., 2013. Automatic drainage pattern recognition in river networks. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 27(12), pp.2319-2342.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Omeed Azad Rafaat, Masoud Hussein Hamed

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.













